In the world of fitness, recovery, and regenerative medicine, few compounds generate as much interest as IGF-1 LR3 (Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Long Arg3). Known for its potential to enhance muscle growth, accelerate recovery, and promote tissue repair, this engineered analog of IGF-1 acts as a longer-lasting and more bioavailable form of the body’s natural growth factor.
When training, recovery, or aging slow your progress, your body needs smarter support. Vita Bella’s IGF-1 LR3 therapy reawakens your natural growth response, helping you restore strength, endurance, and confidence. Because your comeback deserves a scientifically proven foundation. Backed by advanced research, Vita Bella’s IGF-1 LR3 therapy works at the cellular level to enhance muscle repair, boost energy, and accelerate recovery.
What is IGF-1 LR3?
IGF-1 LR3 1 is a modified version of human IGF-1, extended by 13 amino acids and featuring a substitution at arginine-3 to reduce binding to IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs). This design increases its half-life from minutes to several hours, allowing for greater receptor activation in tissues such as muscle and tendon.
While research on IGF-1 LR3 in humans remains limited, human preclinical data 2 and mechanistic studies offer valuable insight into its biological potential and safety profile. This guide explores what IGF-1 LR3 is, how it works, and the benefits and side effects you should be aware of, backed by scientific evidence.
Once bound to the IGF-1 receptor 3 (IGF-1R), it triggers key anabolic pathways such as Akt/mTOR, stimulating protein synthesis, cellular growth, and repair. These mechanisms are central to how IGF-1 contributes to both strength and recovery in human biology.
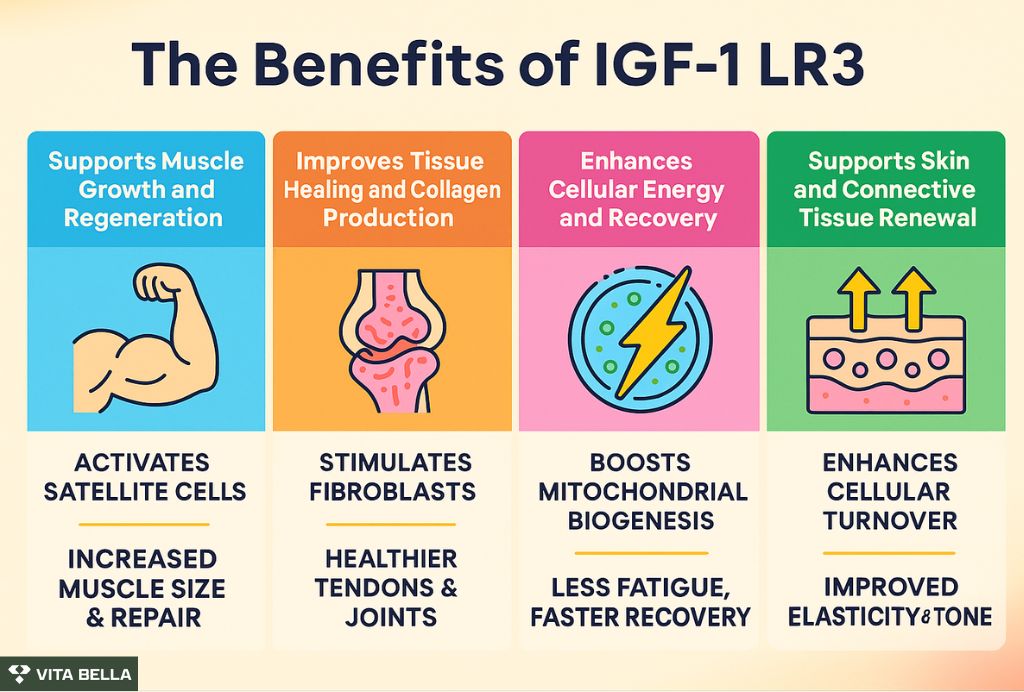
What are the Key Benefits of IGF-1 LR3?
Although large-scale clinical trials are still lacking, multiple human and human-cell studies support IGF-1’s role in tissue repair, hypertrophy, and metabolic balance. Here are the most notable science-backed benefits:
1. Supports Muscle Growth and Regeneration
IGF-1 is a critical factor for muscle hypertrophy and repair. In human muscle cell studies 4, IGF-1 directly increased myotube nuclei, fusion index, and myosin heavy chain content, all key indicators of muscle growth.
Furthermore, human reviews 5 confirm that IGF-1 activates satellite cells, enabling muscle fibers to regenerate after damage or strenuous exercise. This makes IGF-1 LR3 a compelling candidate for supporting recovery and lean muscle maintenance in active adults.
2. Improves Tissue Healing and Collagen Production
IGF-1 accelerates tissue repair by enhancing collagen synthesis and cellular remodeling. A human-derived tendon cell model 6 demonstrated increased collagen expression and improved matrix structure following IGF-1 exposure, showing potential benefits for joint and tendon recovery.
Because IGF-1 LR3 remains active longer than native IGF-1, it may provide extended stimulation of repair pathways, making it particularly valuable for individuals undergoing physical therapy or post-injury rehabilitation.
3. Enhances Cellular Energy and Recovery
IGF-1’s activation of the Akt/mTOR pathway not only builds new tissue but also optimizes mitochondrial biogenesis, the process of creating new mitochondria. In human metabolic research 3, elevated IGF-1 levels correlated with improved muscle energy utilization and reduced fatigue during recovery phases.
By supporting both anabolic growth and energy metabolism, IGF-1 LR3 contributes to a faster and more complete recovery process.
4. Supports Skin and Connective Tissue Renewal
In human dermal fibroblast studies 7, IGF-1 improved cellular proliferation and collagen remodeling, processes that underlie skin elasticity and repair. These findings elucidate its potential role in aesthetic and regenerative treatments designed to enhance skin tone and texture.
5. Promotes Cognitive and Neurological Function
Preclinical human neural models8 have shown that IGF-1 supports neurogenesis and neuronal repair. Increased IGF-1 signaling has been associated with enhanced cognitive resilience and improved neuroplasticity, particularly in studies related to aging . While LR3-specific data are still emerging, these mechanisms indicate possible neuroprotective effects.
What are the Potential Side Effects of IGF-1 LR3?
Like all potent biological compounds, IGF-1 LR3 should be approached carefully. Preclinical and observational data suggest that side effects primarily depend on dosage, frequency, and individual metabolic response. Reported or potential effects include:
Hypoglycemia: IGF-1 enhances glucose uptake by muscles, which can occasionally lead to transient low blood sugar, especially when fasting or undernourished.
Water retention: Mild edema has been reported in association with IGF-1 administration, likely due to increased cellular hydration.
Joint or muscle tightness: Rapid tissue hydration and growth can cause temporary stiffness or mild discomfort.
Insulin sensitivity changes: Prolonged high doses may affect insulin signaling; however, human data remain limited and inconsistent.
Accelerated Growth of Pre-Existing Cancers
IGF-1 may accelerate tumor progression, especially in tissues sensitive to hormonal or growth signaling (e.g., breast, prostate, colorectal).Potential for Acromegaloid Features at Excessive Doses
Chronic supraphysiologic IGF-1 levels can mimic growth hormone excess.
Possible signs include jawline prominence, enlarged hands/feet, coarse facial features, and organ enlargement (rare and associated with long-term abuse).
Best Practices and Monitoring
To ensure optimal outcomes, experts recommend pairing IGF-1 LR3 or any growth-factor therapy with lifestyle and medical guidance:
Medical oversight: Always begin therapy after baseline hormone and glucose testing.
Gradual progression: Start with clinically validated low doses.
Nutrition alignment: Maintain a balanced intake of protein and carbohydrates to support IGF-1-driven growth.
Periodic blood work: Monitor fasting glucose, IGF-1, and lipid profile every 3–6 months.
Holistic support: Combine with resistance training, proper sleep, and recovery strategies for best results.
Experience Faster Muscle growth, Healing and Cognitive Function with Vita Bella - Get Yours Now
Every rep counts until fatigue, soreness, and slow recovery hold you back. Vita Bella’s IGF-1 LR3 solution helps your body recover smarter by supporting muscle regeneration, collagen repair, and balanced hormone function. Push past limits and perform stronger than ever, powered by precision wellness. Reclaim your strength, restore your balance, and experience what it truly means to perform and recover at your peak with Vita Bella.
FAQs
Is IGF-1 LR3 effective for muscle growth?
Yes, IGF-1 LR3 activates key anabolic pathways, such as Akt/mTOR, that drive protein synthesis and muscle fiber repair. Human preclinical studies show that IGF-1 increases myotube nuclei and muscle protein content, leading to enhanced muscle growth and recovery.
Can IGF-1 LR3 help improve recovery after exercise or injury?
Yes, IGF-1 LR3 promotes tissue regeneration by stimulating collagen production and activating satellite cells. Human tendon and fibroblast studies demonstrate improved healing and matrix remodeling, making it beneficial for faster recovery.
Are there any side effects associated with IGF-1 LR3?
Yes, some users may experience mild effects, such as temporary hypoglycemia, water retention, or muscle tightness, due to enhanced cell hydration. However, these effects are generally manageable and reversible under medical supervision.
Is IGF-1 LR3 safe to use long-term?
No, long-term safety data in humans are limited. While short-term human preclinical studies indicate beneficial effects on muscle and tissue repair, ongoing medical monitoring is essential to maintain balanced hormone and glucose levels.
References:
Thomas, A., Walpurgis, K., Delahaut, P., Fichant, E., Schänzer, W., & Thevis, M. (2017). Determination of LongR3-IGF-I, R3-IGF-I, Des1-3 IGF-I and their metabolites in human plasma samples by means of LC–MS. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 138, 68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2017.01.030
Yang, Y., Wu, J., & Watson, J. T. (2005). Probing the folding pathways of long R3 insulin-like growth factor-I (LR3IGF-I) and IGF-I via capture and identification of disulfide intermediates by cyanylation methodology and mass spectrometry. Biochemistry, 44(27), 8970–8982. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi050232p
Barclay, R. D., Burd, N. A., Tyler, C., Tillin, N. A., & Mackenzie, R. W. (2019). The role of the IGF-1 signaling cascade in muscle protein synthesis and anabolic resistance in aging skeletal muscle. Frontiers in Nutrition, 6, 146. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2019.00146
Jacquemin, V., Furling, D., Bigot, A., Butler-Browne, G. S., & Mouly, V. (2004). IGF-1 induces human myotube hypertrophy by increasing cell recruitment. Experimental Cell Research, 297(1), 148–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.03.035
Yoshida, T., & Delafontaine, P. (2020). Mechanisms of IGF-1-mediated regulation of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy. Cells, 9(9), 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9091970
Miescher, I., Rieber, J., & Calcagni, M. (2023). In vitro and in vivo effects of IGF-1 delivery strategies on tendon healing: A review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(3), 2370. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032370
Kok, H. J., & Barton, E. R. (2021). Actions and interactions of IGF-I and MMPs during muscle regeneration. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 119, 48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2021.04.015
Forcina, L., Miano, C., Scicchitano, B. M., & Musarò, A. (2019). Signals from the niche: Insights into the role of IGF-1 and IL-6 in modulating skeletal muscle fibrosis. Cells, 8(3), 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8030232





















